Another simple and quick fix is to weld a noncolliding transparent part to the original part, which is the same size but a little bit bigger, then use a .Touched event for the transparent part (not reliable though, touched is garbage)
hey, i use your code but. like the topic of this forum. how did i check where the surface is colliding
like if the right is colliding, i you cant press “D” to move. vice versa
UserInputService.InputStarted
if rayIsTouchingRight ~= true and Enum.KeyCode.D then …
yea from that code, how to return where surface are colliding
HumanMop’s way is actually good, only bad thing is you won’t know which side/edge is the “bad” one touching, maybe make the transparent, bigger, block, and make 4 walls? And depending which wall the bigger block touches disable a input?
This will also fix weird issues if you ran to wall edges
yea, thx for the help too. 
I will make you a drawing 30000000 chars
I would probably change the entire approach to input reading that you are using. Throwing strings into and pulling them out of an array based on which keys are down isn’t necessary to keep up with the input situation, you could handle it more cohesively like UMirinBrah suggested.
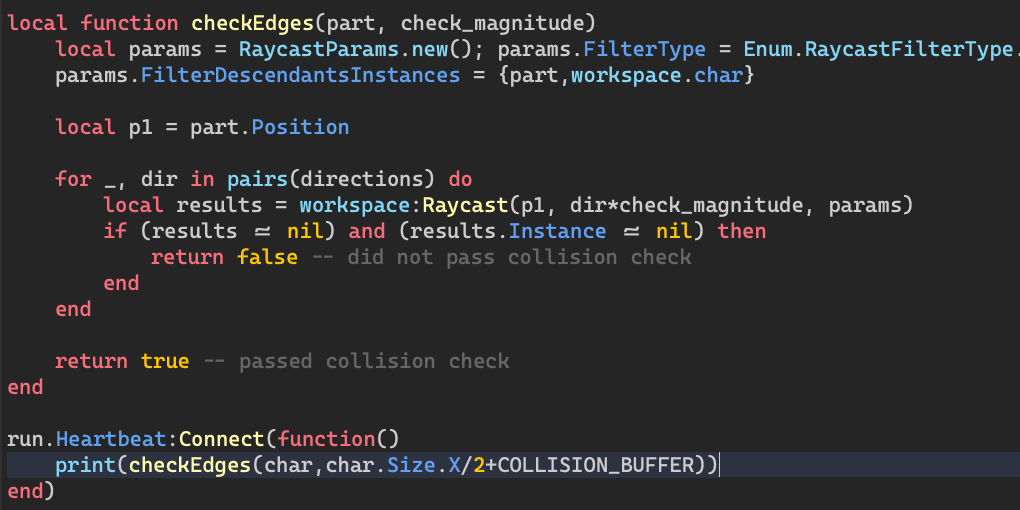
I believe this checking method should be more useful, didn’t test lmk
local directions = {
Vector3.FromNormalId(Enum.NormalId.Front);
Vector3.FromNormalId(Enum.NormalId.Back);
Vector3.FromNormalId(Enum.NormalId.Left);
Vector3.FromNormalId(Enum.NormalId.Right);
}
local function checkEdges(part, check_magnitude)
local params = RaycastParams.new(); params.FilterType = Enum.RaycastFilterType.Blacklist
params.FilterDescendantsInstances = {part,workspace.char}
local p1 = part.Position
local size = part.Size.X / 2 -- this is assuming the part's X and Z dimensions are equal to each other
-- iterate through the part's edges and centers
for x = -1, 1 do
for z = -1, 1 do
local cast_location = p1 + Vector3.new(size*x,0,size*z)
for _, dir in pairs(directions) do
local specificCheckLength = check_magnitude
if x == 0 and z == 0 then
specificCheckLength = size + check_magnitude
end
local results = workspace:Raycast(cast_location, dir*specificCheckLength, params)
if (results ~= nil) and (results.Instance ~= nil) then
return false, results.Position -- did not pass collision check, pass false and location of collision
end
end
end
end
return true -- passed collision check
end
You can use HumanMop’s script or if you’d rather, you could use a block that is a little bit bigger than your original block, in this case the black one is our false block, this block would be welded and would check everything near the part
Use .Touched and.TouchEnded to determine which walls (the coloured walls) are being touched and add them to a dictionary
local isHitting = {
[“Right”] = true,
…
}
if input.KeyCode == Enum.KeyCode.D and isHitting[“Right”] ~= true then
MoveRight()
end
This is just pseudo-code btw